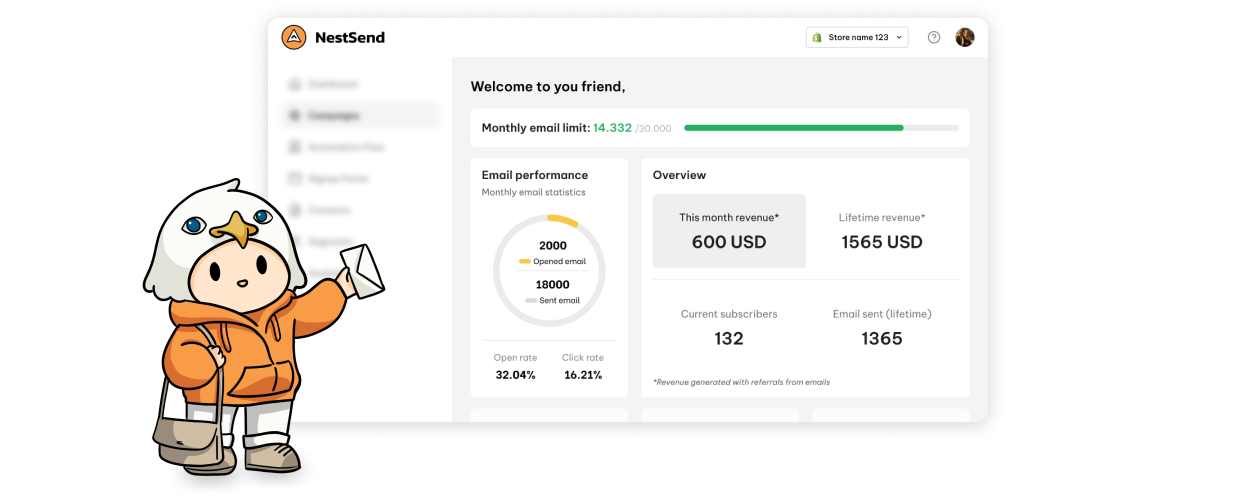
Tracking and analyzing marketing metrics is essential for businesses aiming to maximize their ad spend and understand customer behavior. In this pursuit, there’s an ongoing debate between two popular models—multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling—each offering unique insights for optimizing marketing strategies.
In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between MTA vs MMM, when to use each model, and how e-commerce businesses—particularly those using Shopify—can leverage these models to optimize their ad spend and improve customer journey insights.
What is multi-touch attribution (MTA)?
Multi-touch attribution is a marketing analysis methodology that assigns credit to individual touchpoints in a customer’s journey that contributes to a conversion. It allows businesses to evaluate the role of various interactions—such as ads, emails, and website visits—and determine their impact on driving customer actions.
Mechanics of multi-touch attribution
- Touchpoint weighting: Multi-touch attribution assigns credit to touchpoints using models like Linear, Time Decay, or Position-Based, based on their role in the customer journey.
- Data tracking: It relies on user-level tracking across channels to provide detailed insights into customer interactions.
- Model selection: Credit distribution varies by the chosen model, reflecting assumptions about touchpoint influence on conversions.
Practical examples of multi-touch attribution
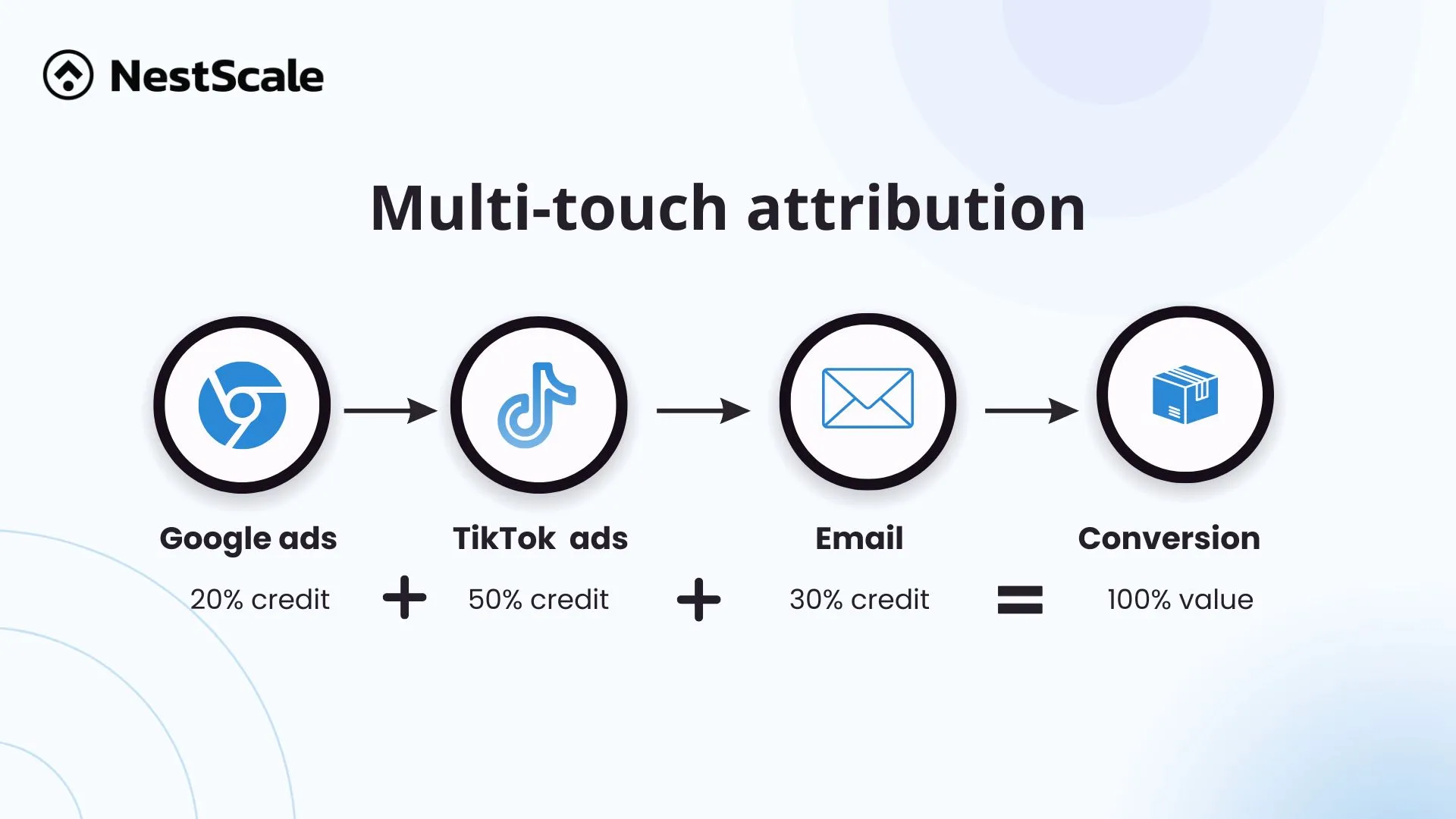
Let’s see how multi-touch attribution can help businesses in a real-life sale. Nestphones, an e-commerce store in the U.S. is selling headphones and a customer named James just bought from the store.
Without Multi-Touch Attribution, the store owner would struggle to understand how James knew about his store, and which of his ads were driving this sale. The shop would only see the final purchase and miss out on crucial insights about how James interacted with different marketing channels.
With multi-touch attribution in place, the store can track James’ journey and identify the role each touchpoint played:
- Google search: James finds and reads a blog post comparing headphones, sparking his initial interest (20% credit).
- TikTok ad: Later, he clicks on a TikTok ad for a model he likes but hesitates to buy because of the price (50% credit).
- Email: Finally, he receives a discount code via email, which prompts him to complete the purchase (30% credit).
These insights allow the store to make actionable adjustments, such as increasing the budget for Facebook ads, optimizing blog content, or improving email discount strategies to boost conversions.
Multi-touch attribution turns scattered touchpoints into a clear, data-driven roadmap for better marketing decisions.
Key types of multi-touch attribution
There are several common models of multi-touch attribution. The 3 most common ones are:
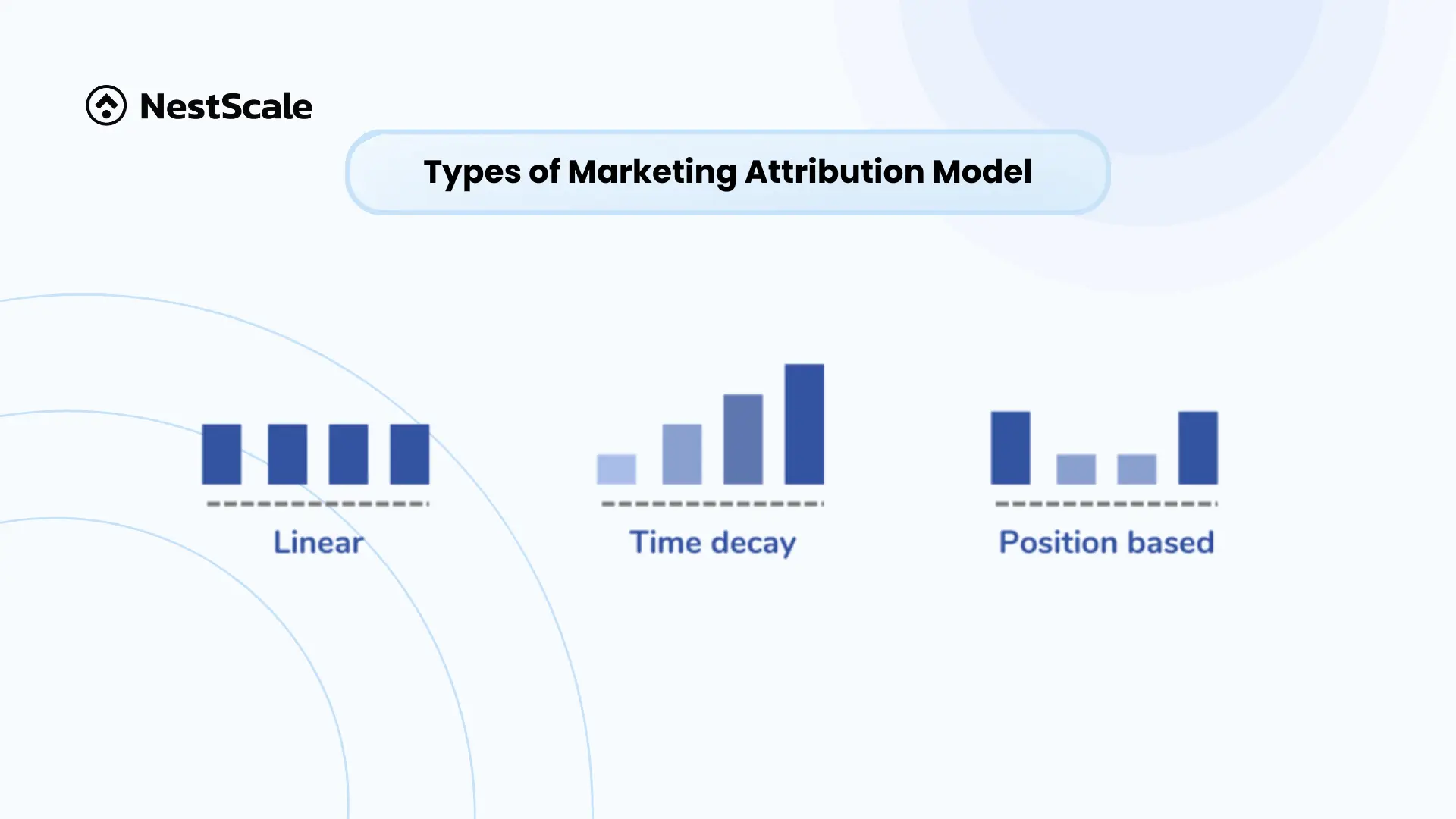
- Linear: Distributes equal credit across all touchpoints in the customer journey.
- Time decay: Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion, favoring recent interactions.
- Position-based: Assigns a higher percentage of credit to the first and last touchpoints while distributing the remainder to touchpoints in between.
Each model offers different insights, depending on the specific goals and structure of a business’s campaigns.
Pros & cons of multi-touch attribution
Gaining insight into the advantages and limitations of multi-touch attribution will help you determine the best times to apply it.
| Pros | Cons |
| Granular insights: Deep understanding of customer journeys by analyzing each touchpoint | Quality data: Requires high-quality, consistent data across all platforms |
| Digital focus: Ideal for tracking digital marketing efforts | Data gaps: Limited by privacy regulations like GDPR for user-level data |
| Cross-channel: Ideal for e-commerce businesses with multi-platform campaigns | Complex setup: May be complex to implement without the right tools |
| Real-time optimization: Enables real-time or near real-time adjustments | Digital bias: Limited ability to account for offline marketing activities |
| Journey mapping: Reflects realistic customer paths, including upper-funnel activities. | Platform limitations: Relies on click data; impression data is often inaccessible. |
TL;DR
Multi-touch attribution is a marketing analysis methodology that assigns credit to each interaction in a customer’s journey, providing businesses with granular insights to optimize their marketing strategies.
Multi-touch attribution relies on user-level tracking and uses various models—such as Linear, Time Decay, and Position-Based—to weight touchpoints based on their influence on conversions.
This approach is ideal for e-commerce businesses, as it transforms scattered data into actionable insights for better decision-making.
What is marketing mix modeling (MMM)?
The mechanism of multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling is fairly different. MMM is an analytical method that correlates marketing spending with overall revenue rather than attributing sales to individual touchpoints.
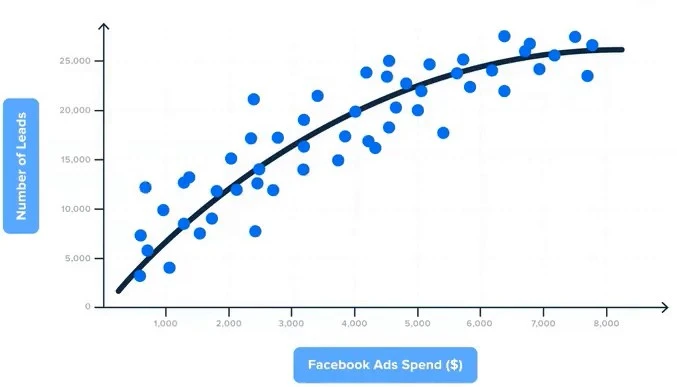
By analyzing aggregated data and adjusting various parameters (e.g. ad spend and impressions), marketing mix modeling helps businesses evaluate the overall outputs of their marketing strategies (e.g. sales performance).
Mechanics of marketing mix modeling
- Regression analysis: Marketing mix modeling uses regression to link marketing inputs (e.g., spend, impressions) with outcomes like revenue.
- Spend-to-revenue correlation: It analyzes how ad spending impacts total sales, focusing on overall performance rather than individual interactions.
- Scenario testing: Businesses can simulate scenarios to test how changes in spending affect performance, enabling better planning and forecasting.
Practical examples of marketing mix modeling
Let’s get back to our U.S. headphones retailer to see the different results between MMM vs attribution. Now, the shop owner wants to sell 200 headphones in the next 6 months and uses marketing mix modeling to test various strategies. For example:
- Increasing ad spend on Facebook by 10% to analyze whether it results in higher sales compared to allocating the same budget to Google.
- Focusing additional budget on specific regions, such as New York, to predict whether targeting that location would lead to more purchases overall.
By experimenting with these scenarios, the retailer gains insights into which changes are most effective in driving sales for their new headphones.
Key types of marketing mix modeling
While marketing mix modeling generally refers to the aggregate evaluation of channel effectiveness, it can also take different approaches depending on business objectives:
- Time-series modeling: Analyzes historical data to determine the long-term impact of different marketing activities.
- Hierarchical models: Allows for multi-level data analysis, such as viewing data at a regional level while still understanding broader impacts.
- Cross-sectional models: Evaluates marketing impact by comparing data across different segments, such as various target demographics or geographic regions.
Pros & cons of marketing mix modeling
By recognizing both the strengths and weaknesses of marketing mix modeling, you can make informed decisions on when to leverage it effectively.
| Pros | Cons |
| Holistic view: Analysis of marketing performance across channels, including online and offline media. | Data requirements: Requires 18–24 months of historical data, which may be difficult to gather. |
| Strategic planning: Suitable for long-term strategy and budgeting. | Slower feedback loop: Relies on historical data, making it less suitable for real-time adjustments. |
| Incorporation of external factors: Accounts for seasonality, economic conditions, and competitive actions. | Time-consuming: The modeling process is complex and resource-intensive, requiring specialized expertise |
| Testablity: Allows businesses to test scenarios, forecast marketing adjustments. | Limited granularity: Operates at an aggregate level, lacking detailed insights into individual customer journeys. |
TL;DR
Marketing mix modeling uses aggregated data to assess the impact of various marketing channels on overall sales, taking into account factors like seasonality. Common marketing mix modeling models include Time-series, Hierarchical, and Cross-sectional, each providing different views of marketing effectiveness.
Marketing mix modeling is best suited for long-term planning and budget allocation across online and offline channels.
Multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling: Key differences
Between multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling, each offers unique ways to analyze marketing impact. Understanding attribution vs MMM key differences can help you decide which model best aligns with your business needs and goals.
| Factor | Multi-Touch Attribution | Marketing Mix Modeling |
| Data granularity | User-level data across touchpoints | Combined data from multiple channels |
| Speed & timeliness | Near real-time insights, useful for quick adjustments | Retrospective analysis, suited for long-term insights |
| Best use cases | Ideal for digital-first businesses focused on quick ROI | Useful for high-level budget planning and strategy |
| Channel compatibility | Primarily online; focuses on digital touchpoints | Works well for both online and offline channels |
| Privacy considerations | Can be limited by privacy regulations like GDPR | Less affected by user-level privacy restrictions |
TL;DR
Multi-touch attribution focuses on user-level data for real-time insights, which is ideal for digital-only channels, while marketing mix modeling uses aggregated data to assess overall marketing effectiveness across all channels, including offline, for long-term planning.
When to use multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling
Choosing between multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling depends on key factors like level of detail, timeframe, channels, data, budget, business scale, and tool costs. Below is an overview to help determine when each model is most effective.
- Business scale: Multi-touch attribution is affordable and ideal for small to medium-sized businesses with digital-first strategies.
Meanwhile, marketing mix modeling is better for larger organizations with higher budgets and complex, multi-channel campaigns. - Tool prices: MTA tools are generally more affordable, making them accessible for small to medium-sized businesses. Pricing tiers often start at around $49 per month for entry-level solutions and can go up to $2000 per month for enterprise-level platforms. In contrast, MMM tools are significantly more expensive, and often designed for larger enterprises with complex marketing strategies. Pricing range from approximately $1,100 up to $3,300 per month.
- Timeframe for insights: Multi-touch attribution delivers near real-time insights, enabling quick adjustments for live campaigns. Marketing mix modeling uses historical data for long-term trends, making it ideal for planning and resource allocation.
- Marketing channels & campaign type: Multi-touch attribution excels in digital-first campaigns, focusing on online interactions like social media and email. Marketing mix modeling suits businesses combining online and offline channels, accounting for factors like seasonality and economic conditions.
- Data availability and requirements: Multi-touch attribution requires user-level tracking and high-quality digital data but may face privacy challenges. Marketing mix modeling needs 18–24 months of historical, aggregated data, which can be challenging for smaller businesses.
TL;DR
Use multi-touch attribution for granular, real-time insights into individual customer interactions, ideal for digital-first campaigns requiring quick optimization and small-medium budget.
Choose marketing mix modeling for holistic, long-term analysis across multiple channels, including online and offline, especially when accounting for external factors like seasonality or market trends and medium-large budget.
MTA vs MMM: Choose the right methods to utilize your data
In the multi-touch attribution vs marketing mix modeling debate, both have their strengths, but the best choice depends on your business size and goals. If you’re an e-commerce SME, consider starting with MTA first to utilize your current data pool and ensure the best accuracy.
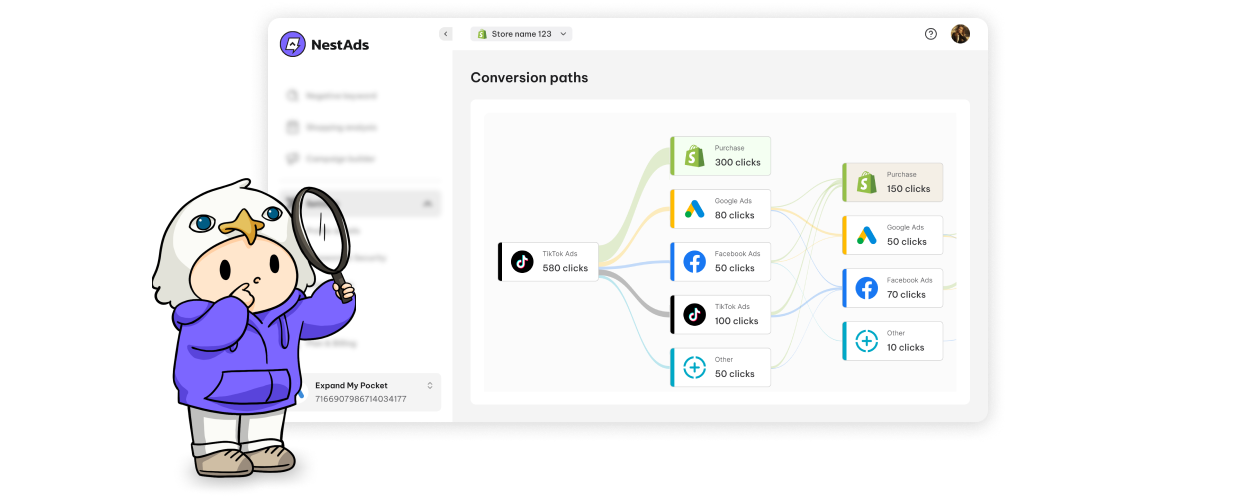
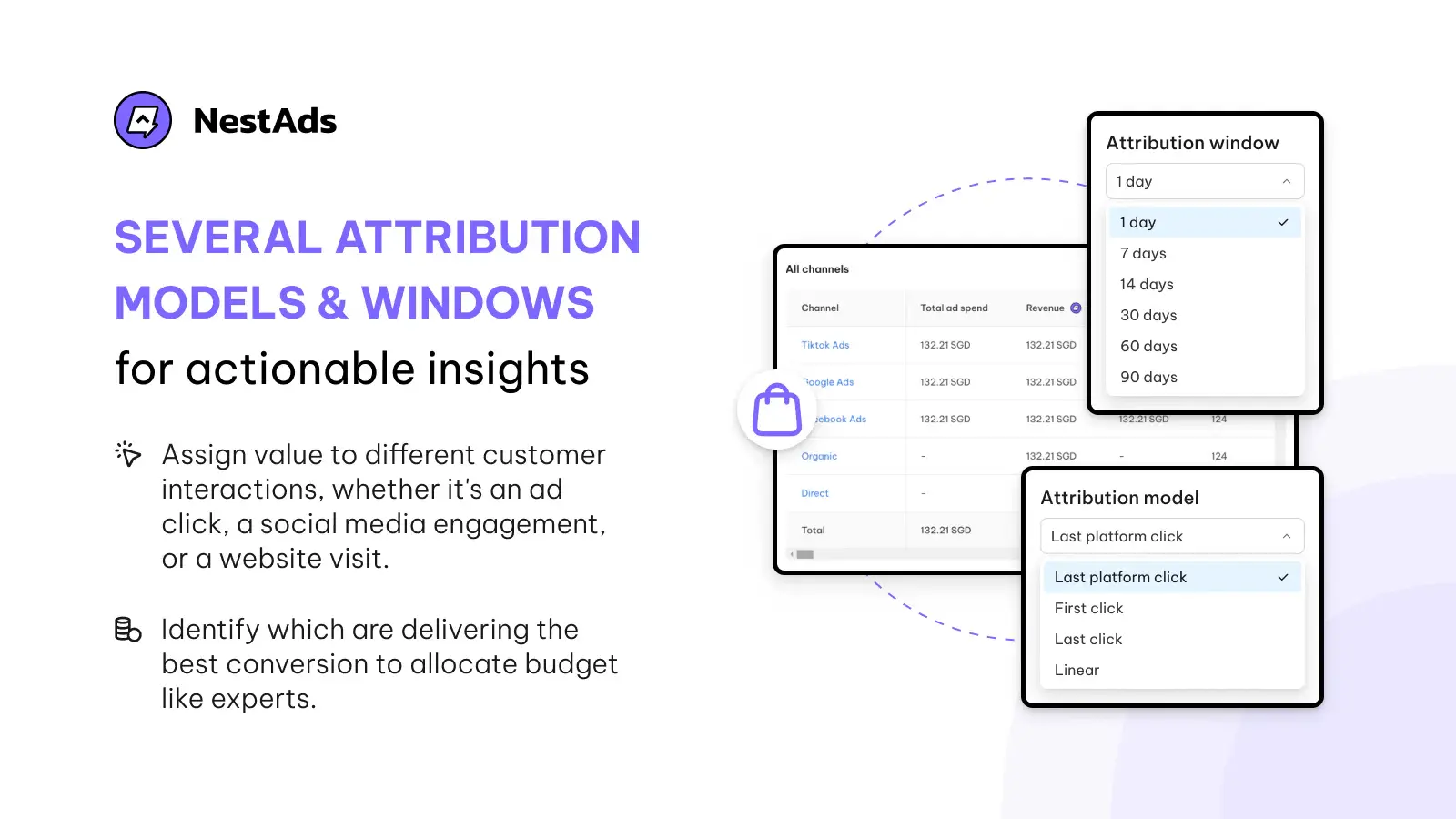
Just centralize your data, choose the best-fit tools to your budget, and you’re good to go! That’s where NestAds comes in. Designed for Shopify merchants, it simplifies MTA implementation and maximizes its benefits.
Here’s how NestAds provides value to e-commerce businesses:
- Numerous multi-touch & single-touch attribution models
- Data centralization in one dashboard
- Customer journey mapping
- User-friendly interface
- Cost-effective pricing
Ready to optimize your ad spend and get detailed insights into your customer journey?
Get started today and see how NestAds can empower your marketing strategy with actionable insights across your key ad platforms.