In a landscape where privacy regulations are becoming more stringent, the use of third-party cookies is undergoing significant changes. Google’s recent announcement to reverse its decision to phase out third-party cookies in Chrome, opting instead for a new approach that grants users more control over their web browsing privacy, marks a pivotal shift. This decision aims to balance privacy concerns with the needs of the advertising industry, allowing for continued development of the Privacy Sandbox and fostering informed choices for users.
As the advertising industry adapts to these evolving dynamics, the focus on first-party data – the information gleaned directly from one’s own customers and target audience, becomes increasingly critical. Although the scope of first-party data may be narrower than third-party data, there is a way that organizations can amplify its value and position it as a more viable and financially sound alternative.
In our first-party data series, we will explore how to harness this invaluable resource effectively. This first blog will explain first-party data definition, its importance, and how it can be a cornerstone for future marketing strategies. As we progress through the series, you’ll discover the key strategies for collecting, managing, and leveraging first-party data to enhance your marketing and advertising efforts.
What is first-party data?
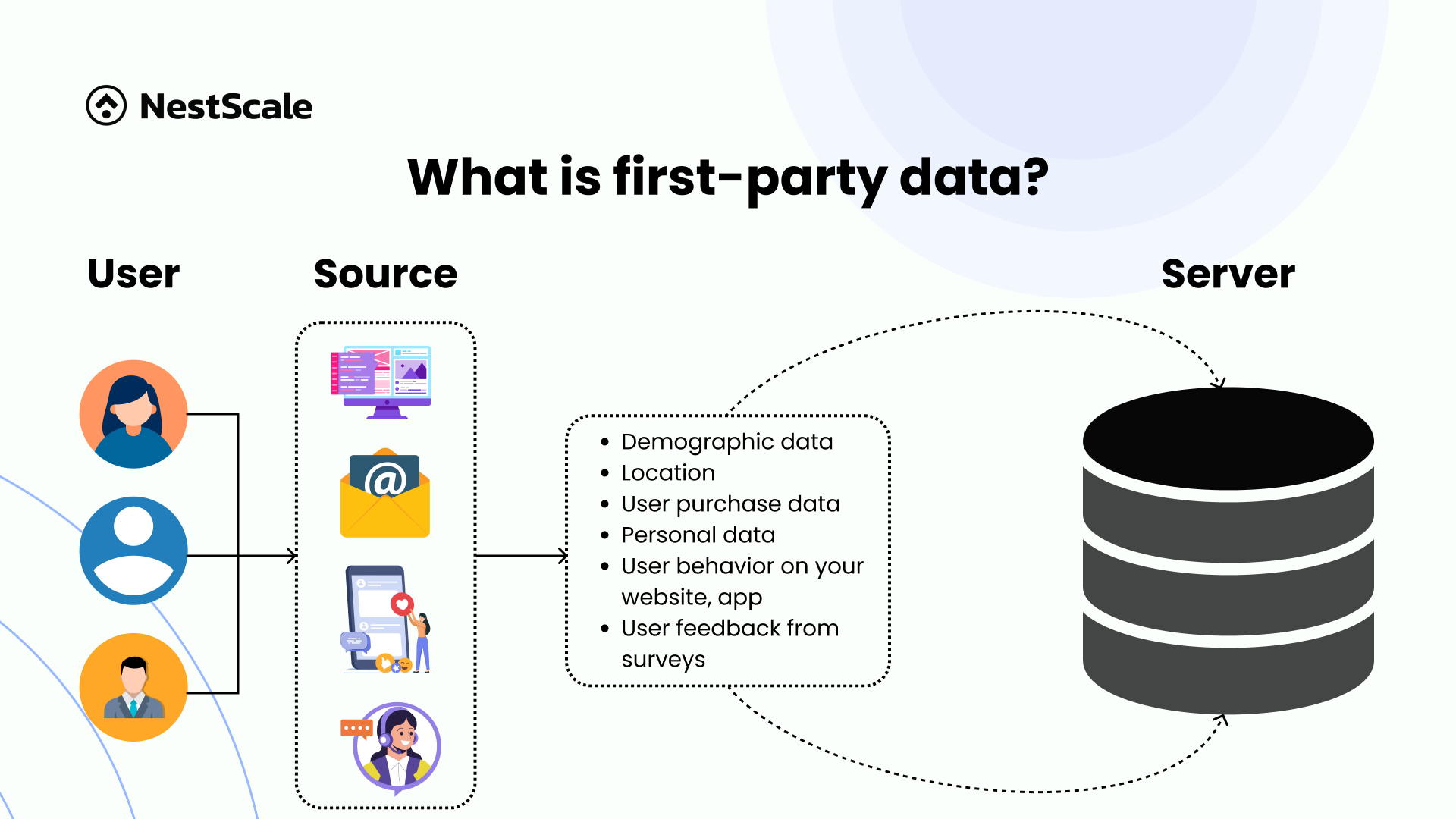
First-party data refers to information collected directly from your audience or customers with their express consent. This data is unique to your business, as there is no intermediary involved in the collection process. It is called the “first-data party” because your business is the first to ask for and obtain this information directly from your users.
After analyzing the definition of first-party data, let’s examine its sources:
- Website interactions: Data collected from user behavior on your website, such as page views, clicks, and time spent on pages.
- Purchase history: Information about past purchases, including what was bought, when, and how often.
- Email subscriptions: Data from email sign-ups, including email addresses and engagement metrics like open rates and click-through rates.
- Social media interactions: Data collected from interactions on social media platforms, such as likes, comments, and shares.
- Surveys and feedback forms: Direct responses from customers through surveys or feedback forms.
Types of first-party data
Understanding the different types of first-party data is crucial for crafting effective marketing strategies and improving customer experiences. First-party data is collected directly from your customers through their interactions with your brand. Here are the main types:
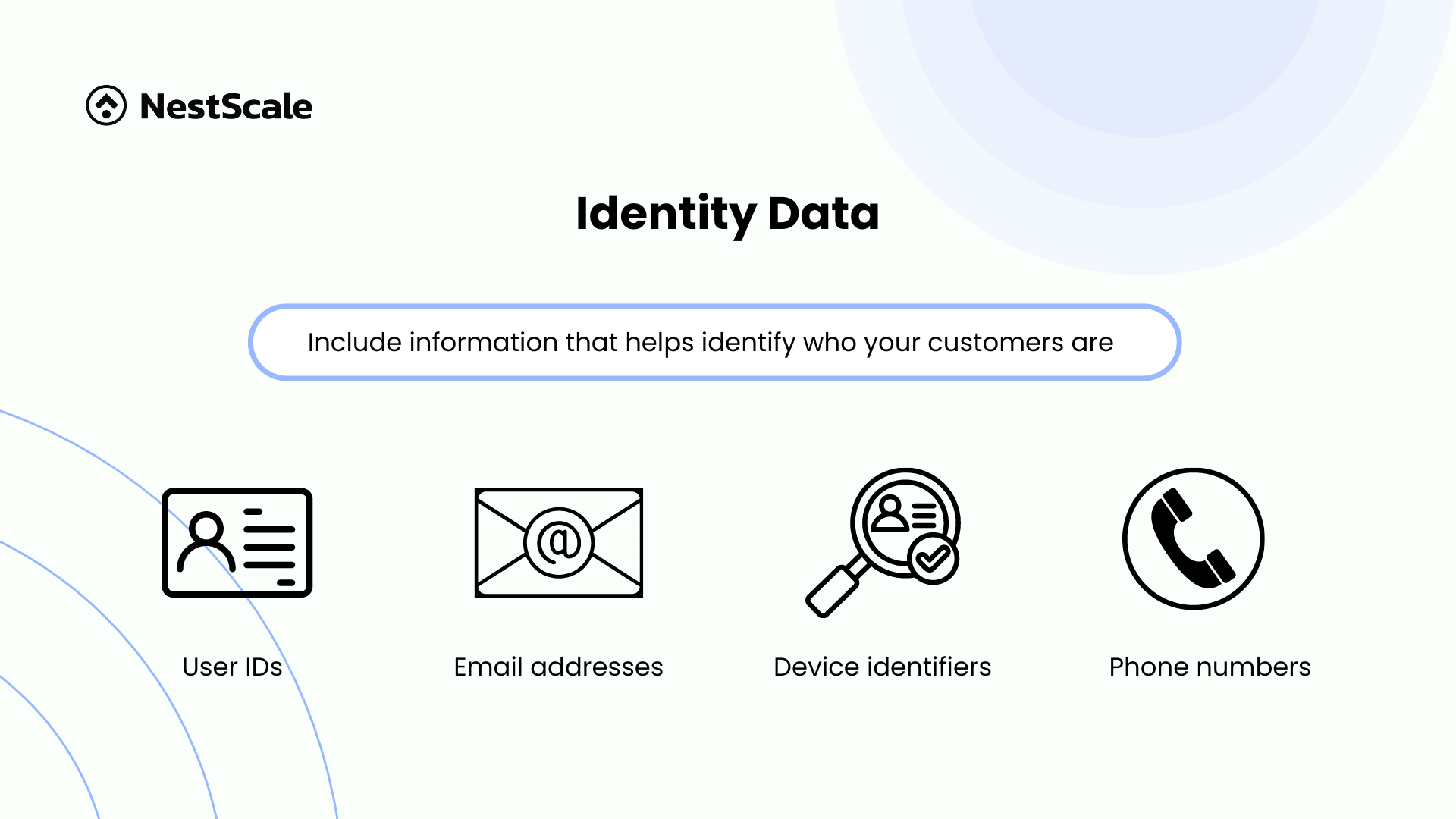
Identity data
Identity data includes information that helps identify who your customers are. This data is often collected during account creation, purchases, or through forms on your website. This type of first-party data includes user IDs, email addresses, device identifiers, first and last names, phone numbers, social handles, loyalty IDs, and more.
Identity data plays a crucial role in any customer data foundation by enabling businesses to establish a unified and accurate view of their customers across various channels and touchpoints.
By identifying individual customers and connecting their interactions and behaviors across multiple devices and platforms, businesses can create a more complete and personalized view of each customer.
There are a variety of ways to use identity data, depending on the nature of your business and the purposes for which the data is collected. Here are some common examples:
- Customer identification and verification: Use identity data to verify customers when creating accounts, making purchases, or accessing services, helping to prevent fraud and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Personalization and marketing: Tailor marketing messages and product offerings based on customer identities, such as using loyalty IDs to provide accurate rewards and special offers.
- Creating accurate audiences: Utilize personal identifiers combined with other data types to ensure accurate audience targeting, ensuring marketing campaigns reach the right individuals.
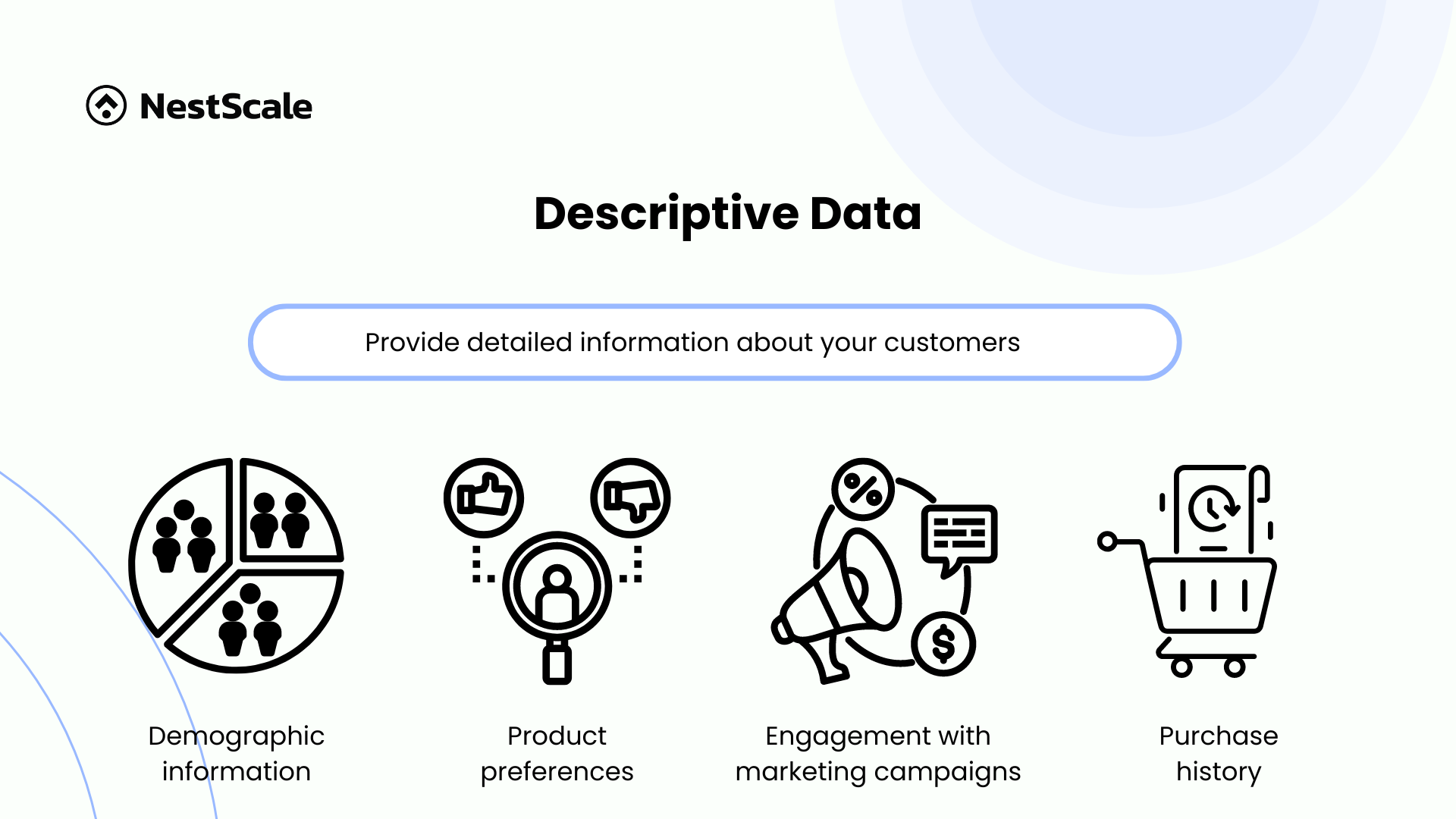
Descriptive data
Descriptive data, a type of first-party data, provides detailed information about your customers. It encompasses demographic details such as age, gender, income level, and education, as well as insights into purchase history, product preferences, and engagement with marketing campaigns.
By collecting and organizing descriptive data effectively, businesses can gain a more nuanced understanding of their customers. This can include specific details such as the type of house they live in, the car they drive, their relationship status, past workplaces, hobbies, and more.
Descriptive data is also valuable for identifying trends and patterns in customer behavior, such as changes in purchase frequency or shifts in product preferences over time. This information can be used to develop targeted marketing campaigns and enhance customer experiences.
Your company can leverage descriptive data to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions across various areas:
- Understand customer behavior: Use data to analyze purchasing habits, preferences, and demographics, enabling targeted marketing, tailored product offerings, and improved customer experiences.
- Evaluate performance: Track KPIs such as sales, revenue, and customer satisfaction to identify performance gaps and implement corrective actions.
- Identify trends: Detect trends in customer behavior and market conditions to anticipate changes and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Benchmarking: Compare performance against industry benchmarks or competitors to identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to catch up.
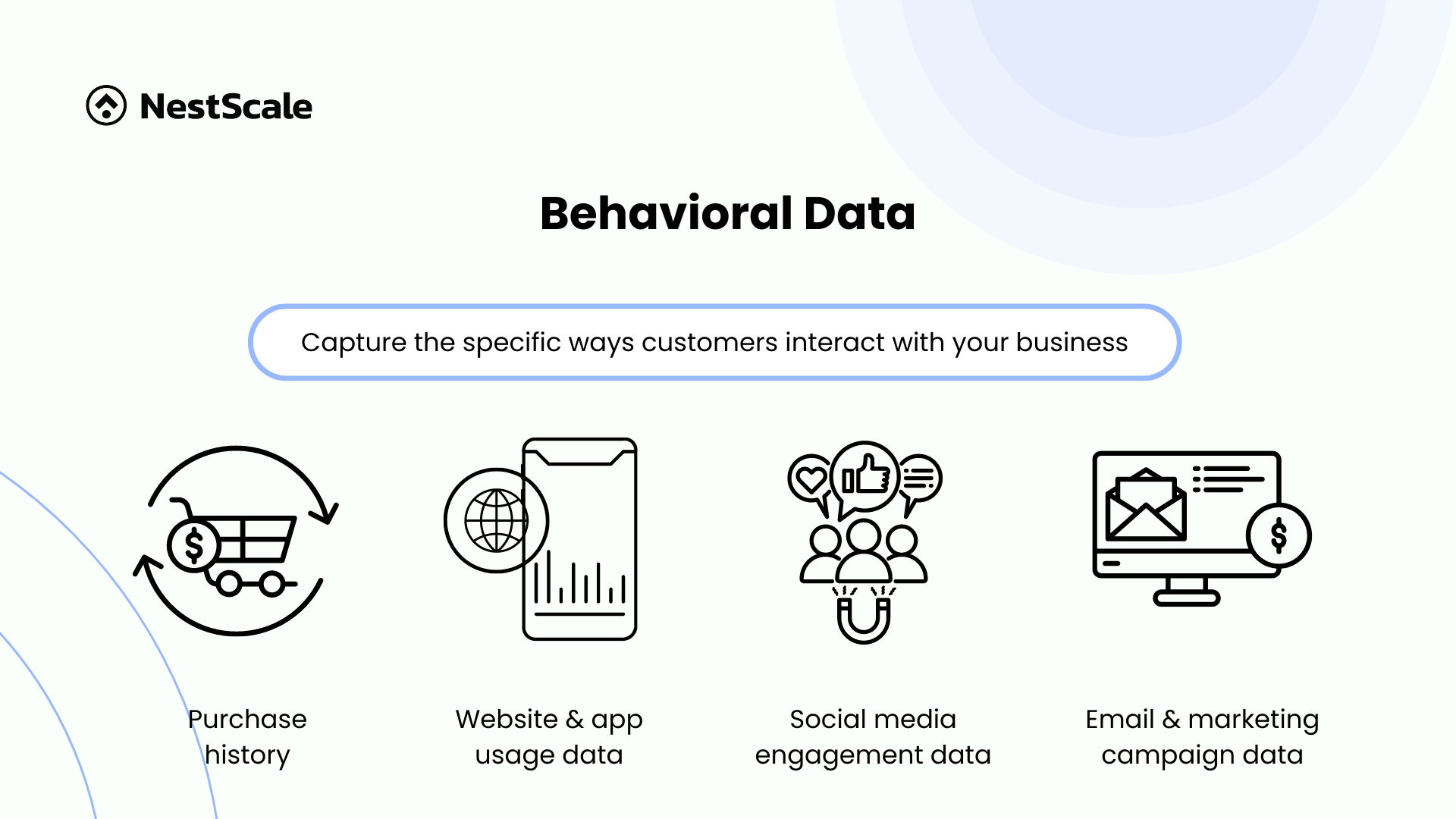
Behavioral data
Behavioral data captures the specific ways customers interact with your business. This includes purchase history, detailing what customers buy, how often, and the value of their transactions. Website and app usage data shows how customers navigate your digital platforms, including page visits, time spent, and actions taken.
Another type of behavioral data is social media engagement data, which tracks interactions on social media, like likes, comments, and shares. Lastly, email and marketing campaign data reveal responses to marketing efforts, such as open rates and click-through rates.
Analyzing behavioral data helps identify patterns and trends in customer behavior and preferences. This enables businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns, improve product offerings, and enhance customer experiences, leading to better customer satisfaction and business growth.
Behavioral data offers numerous opportunities for gaining valuable insights. Using this type of first-party data, businesses can:
- Retargeting: Use behavioral data to retarget customers who have shown interest but haven’t completed a purchase, increasing the chances of conversion.
- A/B testing: Conduct A/B testing to determine which version of a product or website drives better customer engagement and conversions.
- Personalized marketing campaigns: Create targeted marketing campaigns based on individual customer preferences and behavior, such as personalized product recommendations or specific promotions.
- Enhanced customer experiences: Improve customer experiences by identifying and addressing areas of friction in the customer journey, such as optimizing the user interface or streamlining the checkout process.
Qualitative data
Qualitative customer data provides insights into the opinions, attitudes, and experiences of customers, typically gathered through open-ended questions and feedback. Understanding this type of 1st party data definition is essential for analyzing customer needs and preferences on a deeper level, which can inform and guide business decisions.
Qualitative data can be collected in various forms, including feedback from surveys, interviews, focus groups, transcripts of customer service interactions, online reviews, social media posts, and customer stories or case studies.
Utilizing qualitative data is complex yet invaluable for understanding customers’ true motivations. By analyzing this first-party customer data, businesses gain deeper insights into customer needs and preferences. This action allows them to tailor marketing, product development, and customer service efforts accordingly. Qualitative data is particularly beneficial for identifying areas for improvement, fostering innovation, and creating customer-centric strategies.
A company can use qualitative customer data to gain insights into customer needs and preferences, enhancing business strategies in various ways:
- Improve product development: Utilize customer insights to gather valuable feedback on product design and features, identifying areas for improvement or innovation.
- Enhance customer service: Analyze qualitative data like customer service call transcripts to identify common issues and frustrations.
- Develop targeted marketing campaigns: Understand customer preferences and interests to create more effective marketing campaigns.
- Build customer loyalty: Use qualitative data to uncover factors driving customer loyalty and engagement.
Why does first-party data matter?
First-party data stands out for its reliability, accuracy, and ethical collection practices. According to Google’s findings, businesses leveraging first-party data for marketing purposes achieved significant revenue increases of up to 2.9 times and cost savings boosted by 1.5 times, highlighting its effectiveness in driving business growth and efficiency.
Here are details on how 1st-party customer data matters significantly for businesses especially e-commerce businesses (in advertising) at the moment:
- Accuracy and reliability: First-party data is collected directly from your customers or users, ensuring its accuracy and reliability. This data comes straight from the source, providing a clear and unfiltered view of customer interactions and behaviors.
- Customer trust and privacy: With increasing concerns about data privacy and regulations, first-party data is obtained with explicit consent from users. This transparency builds trust and enhances compliance with legal requirements.
- Deeper customer insights: First-party data offers rich insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and purchasing patterns. This enables businesses to create personalized experiences, tailor marketing strategies, and optimize products and services based on real customer feedback.
- Long-term relationship building: By understanding 1st-party data meaning, businesses can foster stronger, long-term relationships with customers through targeted messaging.
- Independence from third-party platforms: Relying on 1st-party data reduces dependency on third-party platforms and their changing policies. This independence gives businesses more control over their data strategies and marketing efforts.
- Improved marketing ROI: With accurate data and targeted marketing efforts, businesses can achieve higher ROI on their marketing campaigns. CDP first-party data enables more efficient use of marketing budgets by focusing on high-value customer segments.
Challenges when using first-party data
One of the main challenges in leveraging first-party data is the collection and integration of data from various touchpoints. Businesses need to ensure that data from websites, mobile apps, and other channels are accurately captured.
Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to incorrect insights and ineffective marketing strategies. Businesses must implement regular data cleansing processes and validation techniques to maintain the integrity of their data.
Moreover, as privacy regulations become more stringent, with 81% of customers feeling they have little to no control over the data collected about them by companies, effectively using first-party audience data offers a competitive edge. Businesses must ensure that their data collection practices comply with laws such as GDPR and CCPA. This involves obtaining explicit consent from users, securely storing data, and providing transparency on how data is used.
Last but not least, as businesses grow, the volume of first-party data increases exponentially. Managing and analyzing large datasets can be challenging without the right tools and technologies. Businesses need to invest in scalable data storage solutions and advanced analytics platforms.
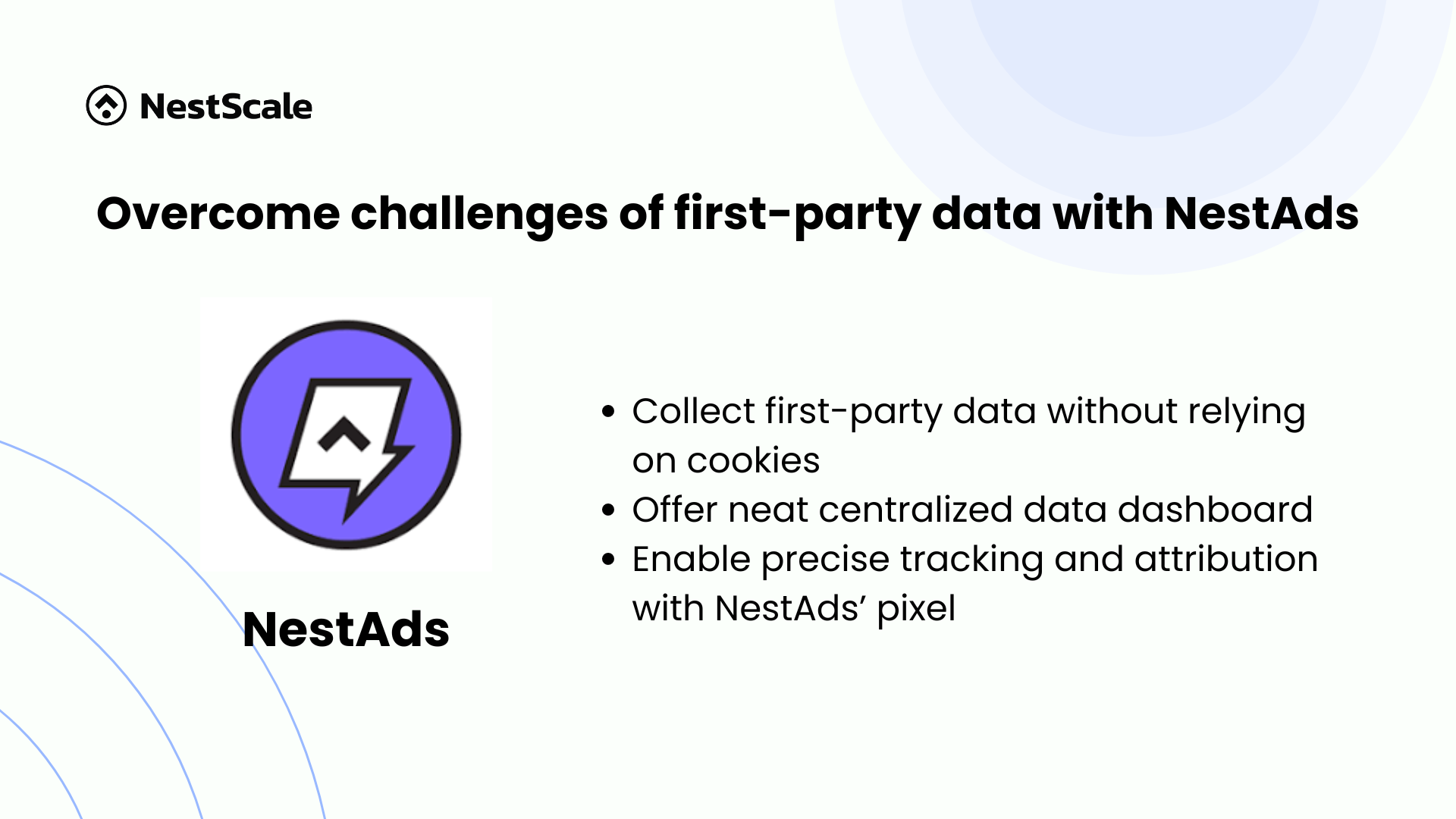
Overcome challenges of first-party data with NestAds
As we prepare to transition away from third-party cookies, the importance of understanding first-party data meaning has never been clearer. However, managing a significant volume of first-party data can be daunting, especially for smaller businesses with limited resources.
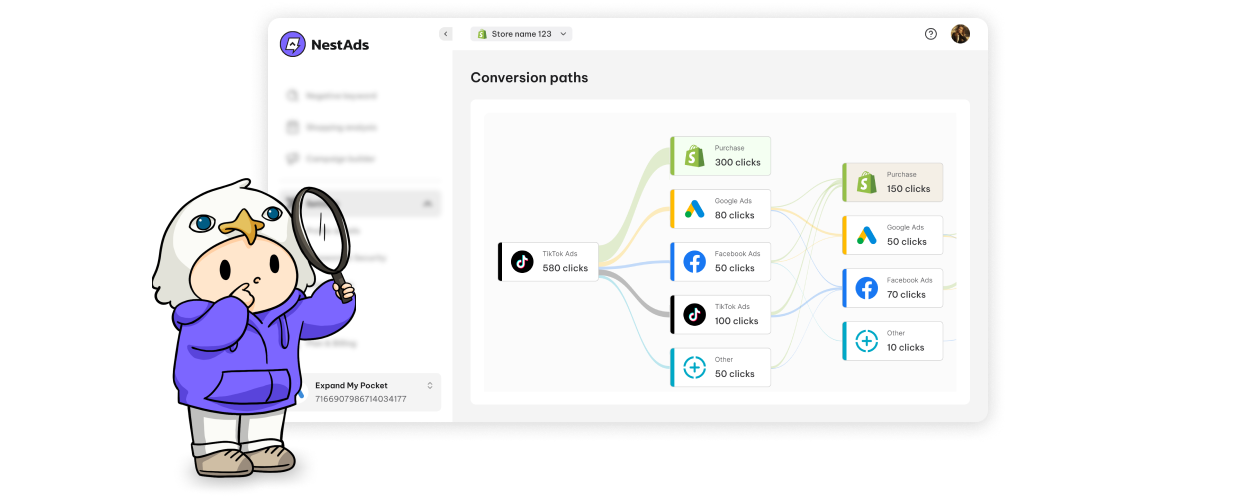
Worry not, with NestAds, navigating this transition becomes streamlined and efficient. NestAds offers a centralized dashboard that seamlessly integrates performance data from multiple advertising channels into one intuitive interface. This simplifies the data analysis process, empowering businesses to gain comprehensive insights without the complexity.
What sets NestAds apart is its resilience in the face of evolving privacy regulations. Unlike third-party cookies, NestAds operates using first-party data gathered with user consent. This approach ensures compliance with stringent privacy standards, including recent updates like iOS 17 Link Tracking Protection. NestAds’ UTMs enable precise tracking and attribution, even amidst tightening privacy restrictions.
With the imminent deprecation of third-party cookies, the clock is ticking for businesses to adapt their online marketing strategies. NestAds stands ready to be your trusted partner in this digital evolution, offering robust solutions to enhance your advertising effectiveness. Embrace the future of digital advertising with NestAds and elevate your marketing efforts with confidence.
In our upcoming second blog, we’ll delve into the differences between zero, first, second, and third-party data. Stay tuned to learn how to navigate this new era of digital marketing responsibly and effectively.