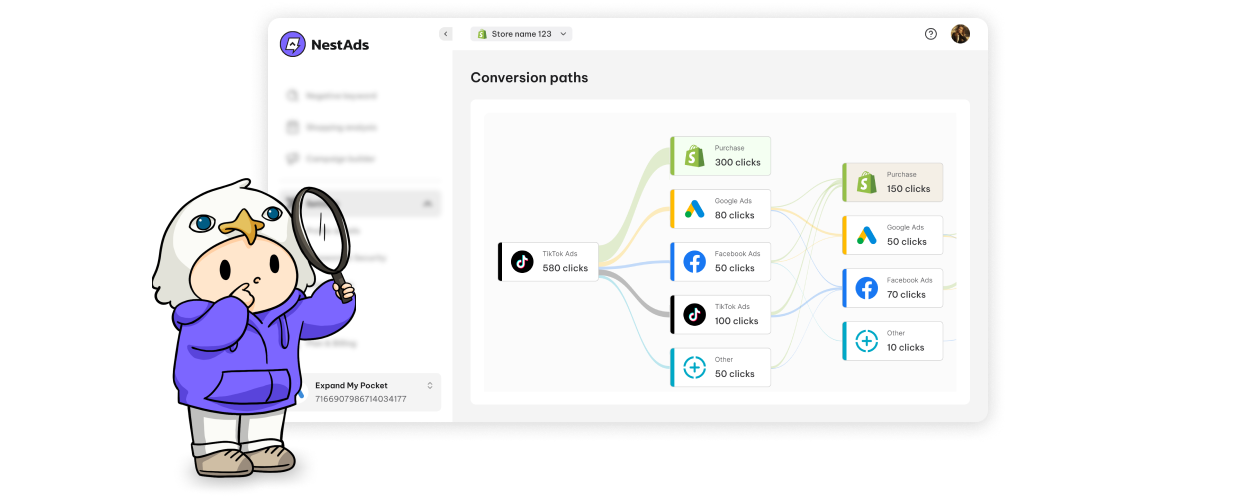
What is user tracking?
User tracking refers to the process of collecting and analyzing data about how users interact with websites, mobile applications, or digital platforms. This data can include various types of user behavior, such as page views, clicks, time spent on a page, purchases, and other interactions. Businesses and marketers use user tracking to understand user preferences, improve the user experience, optimize marketing campaigns, and boost overall performance.
In simpler terms, user tracking enables businesses to see what users do, how they behave, and why they take certain actions. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make informed decisions that align with customer needs and business goals.
Why is user tracking important?
- Understand user behavior: Analyze how users interact with your platform, including clicks, views, and time spent on pages.
- Optimize user experience: Identify pain points and improve usability to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Personalize customer journeys: Deliver tailored content, offers, and experiences based on user preferences.
- Improve marketing strategies: Evaluate campaign effectiveness, identify what works, and allocate budgets more effectively.
- Drive growth: Use insights to make data-driven decisions that improve performance and business outcomes.
How does user tracking work?
User tracking relies on various technologies and tools to collect and analyze data. Here are some of the most common methods:
- Cookies and pixels:
- Cookies: Small files stored in a user’s browser to track their activities, such as login details, shopping cart items, and browsing history.
- Tracking Pixels: Tiny pieces of code embedded in a webpage or email that collect information about user actions, such as clicks or views.
- JavaScript tags: JavaScript tags are snippets of code placed on a website to collect data about user behavior, such as page views, button clicks, and form submissions.
- Session Recording and Heatmaps:
- Session Recording: Records user sessions to show how users navigate a website, providing visual insights into their behavior.
- Heatmaps: Visual representations of where users click, scroll, or hover on a page.
- Analytics tools: Platforms like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Hotjar track user behavior and provide detailed reports on website traffic, conversions, and engagement metrics.
- Server-side tracking: This method involves tracking user actions directly on the server rather than relying on browser-side cookies. Server-side tracking is more accurate, secure, and less impacted by browser restrictions.
Types of user tracking
- Client-side tracking: Tracks user behavior on the user’s browser using cookies, pixels, and tags.
- Server-side tracking: Collects data on the server, offering greater accuracy and privacy.
- Cross-device tracking: Tracks users across multiple devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and desktops, to create a unified customer view.
- Event tracking: Tracks specific actions, such as button clicks, form submissions, and purchases.
Privacy and user tracking
While user tracking offers numerous benefits, it also raises concerns about user privacy. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA require businesses to be transparent about tracking practices and obtain user consent before collecting data.
To build trust with users, businesses should:
- Clearly inform users about data collection practices.
- Allow users to opt in or opt out of tracking.
- Securely store and manage user data.
- Follow regulatory guidelines to ensure compliance.