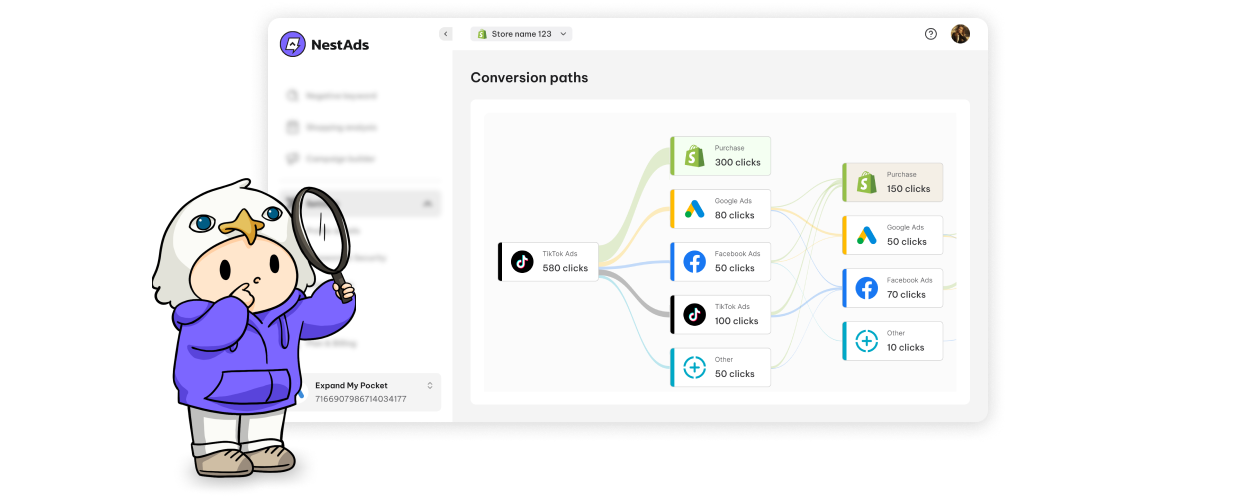
What is marketing experimentation?
Marketing experimentation is the process of testing and analyzing different marketing strategies, campaigns, or tactics to identify what works best for achieving specific business goals.
By systematically changing variables, such as ad creatives, targeting methods, or promotional offers, businesses can measure performance, optimize efforts, and make data-driven decisions.
Why is experimental marketing essential?
Marketing experimentation is essential for staying competitive in a dynamic market environment. Key benefits include:
- Informed decision-making: Replace guesswork with data-backed insights.
- Risk reduction: Test ideas on smaller scales before committing to large campaigns.
- Continuous improvement: Identify what resonates most with customers and refine strategies accordingly.
- Personalization opportunities: Tailor campaigns to specific audience segments based on experimental results.
This iterative approach makes sure your marketing budgets are invested in high-performing strategies that drive measurable results.
What are key steps in marketing experiments?
To conduct effective marketing experiments, businesses can follow these essential steps:
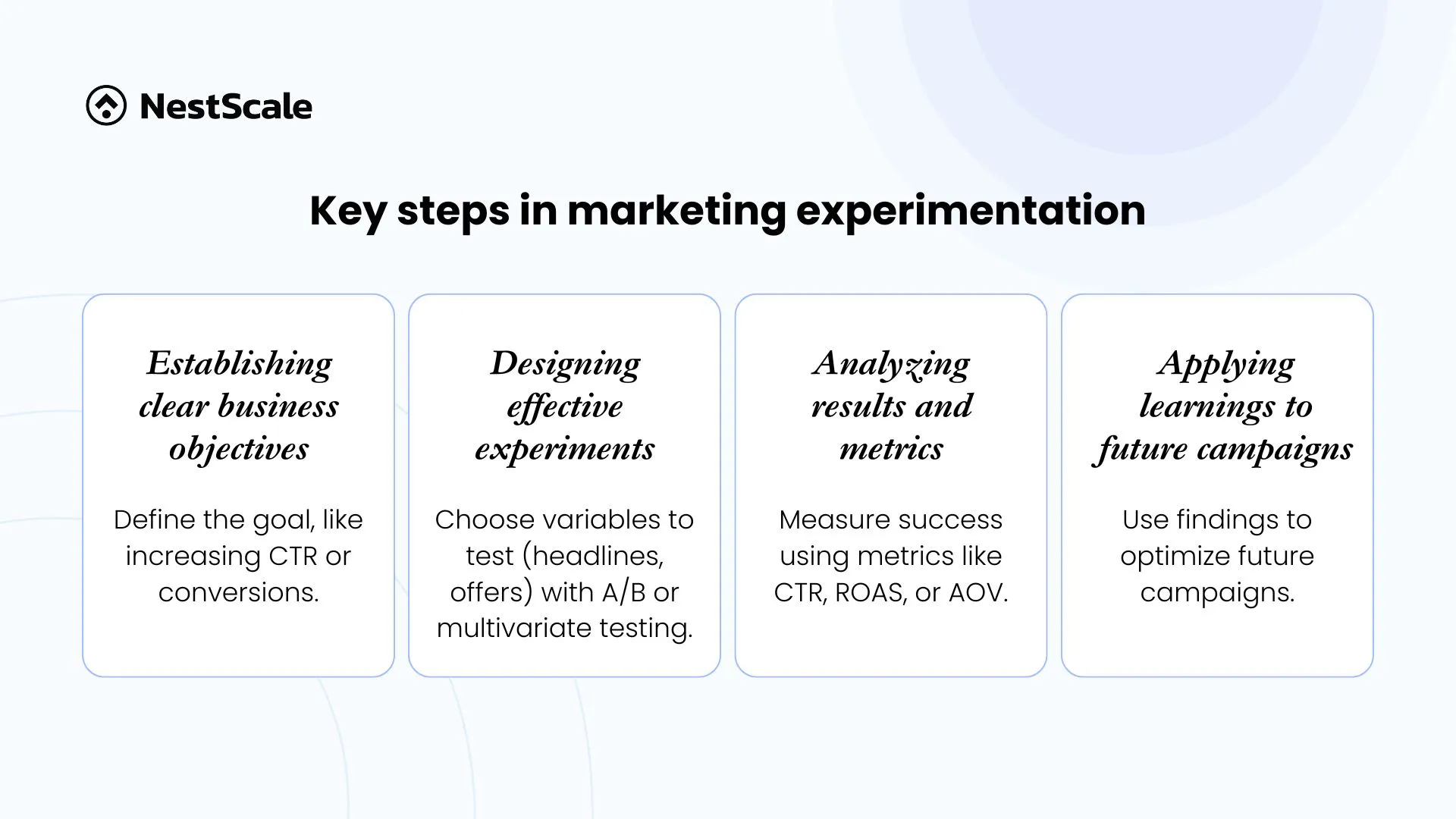
1. Establishing clear business objectives
Every successful experiment starts with a clearly defined purpose. You need to ask whether the experiment aims to increase click-through rates, improve conversion rates, or understand customer preferences. Setting clear objectives can deliver focus and meaningful outcomes.
2. Designing effective experiments
Creating a well-structured test involves identifying the variables to be changed, such as headlines, ad copy, or discount offers. You should maintain consistency across other factors. Common approaches include A/B testing, multivariate testing, or split testing.
3. Analyzing results and metrics
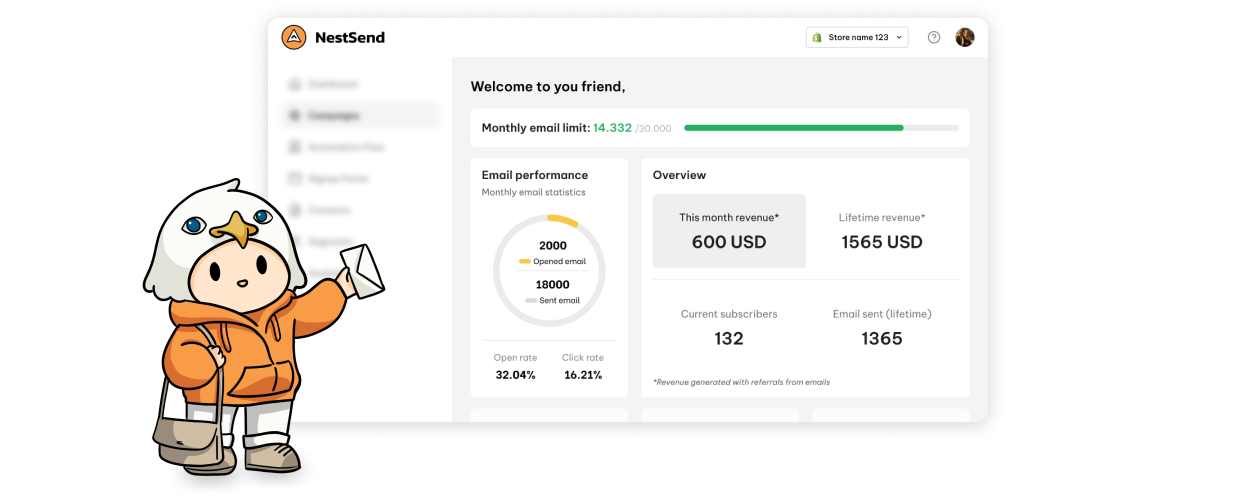
When the experiment concludes, you need to analyze the data to identify statistically significant outcomes. Performance metrics, such as CTR, ROAS, or AOV, provide clear indicators of success for each variation.
4. Applying learnings to future campaigns
The true value of experimentation lies in its application. Businesses should use insights gained from the test to optimize current strategies and guide future campaigns.
What is the framework for successful experiments in marketing?
A structured framework makes experiments deliver actionable insights:
- Start small: You should test one variable at a time to isolate its impact.
- Use control groups: Control groups allow companies to compare results against a baseline.
- Ensure statistical significance: Businesses should avoid making decisions based on insufficient data.
- Document results: Maintaining records helps teams track what works and what doesn’t for future reference.
- Iterate and refine: Teams should view each experiment as a stepping stone for the next.
Marketing experiment ideas for eCommerce
Here are some ideas for eCommerce businesses to conduct marketing experiments and enhance performance:
Test different product page designs
Experiment with layouts, image placement, or call-to-action (CTA) button designs to see what increases conversions. For example, a fashion brand could test whether adding customer reviews near the product description boosts sales.
Experiment with free shipping thresholds
Run tests to determine the optimal free shipping threshold that encourages customers to spend more. For instance, compare $50, $75, and $100 thresholds to see which generates the highest average order value.
Test social media ad formats
Try carousel ads, single-image ads, and video ads on platforms like Facebook or Instagram. Analyze which format drives the highest engagement and ROI for your target audience.
Optimize email campaign timing
Test different days and times for sending promotional emails. For example, an online electronics store could compare open rates for emails sent on Monday mornings versus Wednesday afternoons.
Personalize product recommendations
Use A/B testing to compare personalized product recommendations versus generic recommendations on your homepage. Measure the impact on click-through rates and purchase frequency.
Test checkout process simplification
Experiment with reducing the number of steps in the checkout process. See if simplifying from a multi-step form to a single-page checkout increases completion rates.