What is web attribution?
Web attribution is the process of identifying and assigning credit to the various online interactions that contribute to a desired conversion, such as a purchase, app installation, or email signup.
By analyzing these interactions, web attribution connects user behavior to conversion events. This helps marketers understand which channels, campaigns, or touchpoints are most effective in driving results. Whether it’s through paid ads, organic search, or email marketing, web attribution gives businesses the insights they need to optimize their strategies and maximize ROI.
How web attribution works
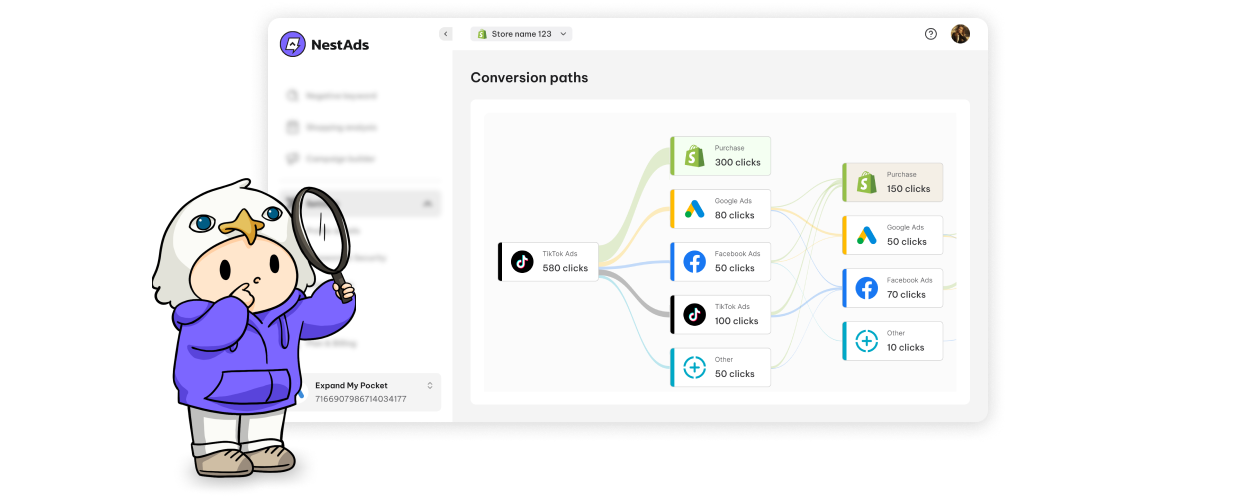
Web attribution operates by gathering and analyzing user web events. These events are attributed to their respective sources through a web SDK (Software Development Kit) embedded in a website. The SDK, a lightweight JavaScript code snippet, tracks user activity such as referrers (the site a user visited prior) or direct traffic, and links it to subsequent conversion events.
- Referrers: Referrers indicate where a user came from – whether it’s an ad, an organic search result, or another website.
- Persistent identifiers: Web cookies or a Customer User ID (CUID) help track users across sessions and devices, linking their actions to conversion events.
For web attribution to function effectively, businesses need a structured attribution flow that includes:
- Cookie-based measurement: Cookies act as temporary identifiers, tracking user activity and linking it to specific channels or campaigns.
- Attribution links: Deep links direct users to specific pages while measuring performance metrics tied to these interactions.
- Measurement parameters: Using UTM parameters or custom tags, marketers collect detailed data about user behavior at every touchpoint.
Common attribution models
Web attribution uses various models to assign credit to different touchpoints in a customer journey. Some of the most common models include:
- Last-click attribution: Credits the final interaction before a conversion. While simple, it overlooks the contributions of earlier touchpoints.
- First-click attribution: Assigns credit to the first interaction. Useful for understanding how users are initially drawn into the funnel.
- Linear attribution: Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints. Ideal for campaigns aiming to evaluate the entire customer journey.
- Time-decay attribution: Assigns more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion event. Suitable for longer sales cycles.
- Position-based attribution: Divides credit between the first and last interactions, with partial credit to touchpoints in between. Effective for journeys with clear entry and exit points.
Uses of web attribution
Web attribution plays a crucial role in modern marketing by:
- Optimizing campaign performance: Identifying high-performing channels and reallocating budgets to maximize impact.
- Improving customer journeys: Analyzing user behavior to remove friction points and improve overall experience.
- Enhancing ROI: Understanding which strategies deliver the best returns helps businesses scale successful campaigns.
- Data-driven decisions: By linking marketing efforts to tangible results, web attribution provides actionable insights for strategy refinement.
Techniques for effective attribution
To tackle challenges such as cross-device tracking and fragmented journeys, marketers employ the following techniques:
- Cookie-based attribution: Tracks user activity within a browser session, enabling precise measurement of individual actions.
- Attribution links: Uses deep linking to connect actions to specific campaigns or web assets, ensuring accurate tracking.
- Unique identifiers: Encourages users to log in or subscribe, creating consistent identifiers like email addresses to unify fragmented data.
- UTM parameters: Adds predefined codes to URLs to track the effectiveness of campaigns, channels, and specific creatives.